Africa stands at a critical economic crossroads. Despite abundant natural resources and a young, growing population, many African nations continue to grapple with currency instability, high inflation, limited banking access, and expensive remittance corridors. These challenges create a perfect storm that keeps millions trapped in poverty while hampering continental economic growth.
In this landscape, bitcoin offers a compelling alternative financial system that addresses many of Africa’s most pressing economic challenges. The continent is already embracing this technology at remarkable rates, with adoption growing faster than global averages in several key markets.
The Current Economic Landscape in Africa
Banking Access Challenges
The lack of traditional banking access remains one of Africa’s most significant economic hurdles. According to recent statistics:
- Approximately 57% of Africa’s adult population remains unbanked as of 2022, compared to just 39% in 2017.
- Around 360 million adults across Africa lack access to any form of bank account, representing roughly 17% of the global unbanked population.
- Banking penetration varies dramatically by country, from over 90% in countries like South Africa to less than 15% in nations like Niger.
The unbanked population faces numerous challenges, including:
- Inability to save securely
- Exclusion from credit markets
- Difficulties receiving payments
- Limited options for wealth preservation
- Vulnerability to theft and loss of physical cash
Remittance Market Size and Costs
Remittances represent a vital economic lifeline for millions of African families and a significant source of foreign currency for many countries.
Key statistics include:
- Africa receives nearly $100 billion in annual remittances, with intra-Africa flows accounting for approximately $20 billion.
- Africa remains the most expensive region globally to send money to, with average costs of 8.37% in Q2 2024 compared to the global average of 6.62%.
- In Q2 2024, remitting from South Africa incurred an average cost of 13.12%, a decrease from its recorded value of 13.18% in Q1 2024.
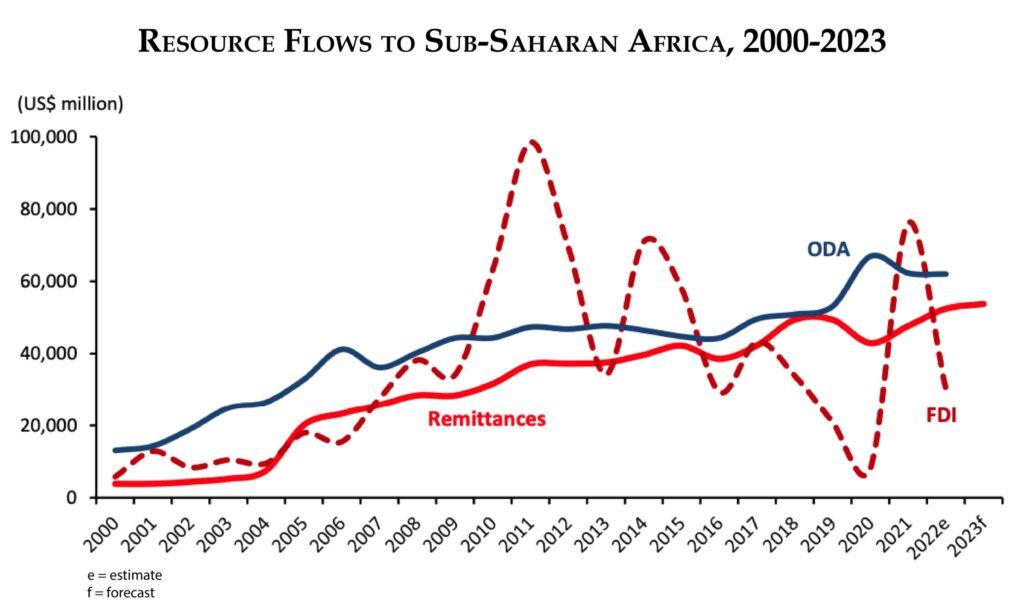
Currency Instability and Inflation
Many African economies suffer from severe currency instability and high inflation rates:
- By the end of 2024, the Nigerian Naira had depreciated 104.38% against the US dollar.
- Several leading African economies, including Kenya and Zambia, saw their currencies tumble by double digits against the US dollar in 2023.
- Zimbabwe’s hyperinflation reached extreme levels—786% in May 2020—creating severe economic hardship.
Bitcoin Adoption in Africa: Current State
Adoption Statistics by Country
Bitcoin adoption is accelerating across Africa:
- Nigeria maintains its position as Africa’s leading digital currency market and ranks second globally in adoption as of 2024.
- South Africa has seen significant growth, with approximately 5.8 million digital currency users, representing 9.4% of the population.
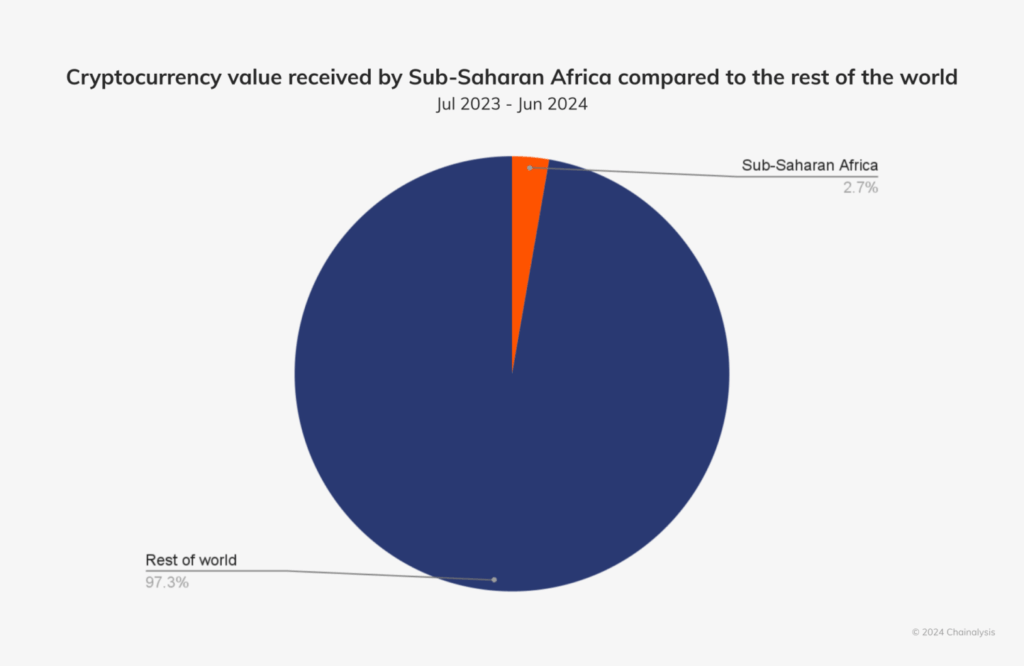
- Sub-Saharan Africa accounts for 2.7% of global digital currency transaction volume as of 2024.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory landscape for bitcoin across Africa varies significantly:
- Only about one-quarter of countries in sub-Saharan Africa formally regulate digital currencies.
- South Africa leads with a comprehensive licensing regime introduced in 2022.
- Nigeria has moved toward allowing digital currencies with the 2025 Nigerian Investment and Securities Bill.
- Kenya is drafting legislation to regulate digital currencies after earlier warnings from its central bank.
- Countries like Cameroon, Ethiopia, Lesotho, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, and the Republic of Congo have implemented outright bans on digital currencies.
How Bitcoin Addresses African Economic Challenges
Banking the Unbanked
Bitcoin offers several advantages for bringing financial services to the unbanked population:
Minimal Entry Requirements
Bitcoin requires only a phone and connection (technologies like Machankura), making it accessible to a much broader portion of the population than traditional banking.
With mobile phone penetration exceeding 50% across most African countries, bitcoin provides a gateway to financial inclusion without the need for physical bank branches or extensive documentation.
Digital Wallets vs. Bank Accounts
Bitcoin wallets offer many functions of traditional bank accounts without the overhead costs, physical infrastructure, or restrictive requirements:
- Self-custody without permission or approval.
- Ability to receive payments from anywhere globally.
- Store value securely with proper security practices.
- Make payments to anyone with internet access.
Reducing Remittance Costs
Bitcoin dramatically reduces the cost of sending money across borders:
Traditional Remittance vs. Bitcoin
- Traditional remittance services to Africa charge an average of 8.37%.
- Bitcoin transactions, particularly using the Lightning Network, can reduce fees to as low as 0.01% to 0.10% of the transferred amount.
- Lightning Network transactions often cost less than a cent, even for cross-border transfers.
Impact on Economic Growth
In Kenya, where the average cost to send $200 is over 8.7%, remittances made up 3.5% of the GDP in 2021, totaling $3.7 billion. Lowering these costs to around 2% could have saved the country over US$200 million, equivalent to 0.22% of its GDP. But it’s not just about economic savings — bitcoin remittances also offer significantly better speed.
Protecting Against Inflation and Currency Devaluation
Bitcoin’s fixed supply and decentralized nature make it an attractive hedge against local currency devaluation and inflation:
Bitcoin as an Inflation Hedge
- Bitcoin’s capped supply of 21 million coins creates scarcity that contrasts with inflationary fiat currencies.
- Bitcoin’s design makes it resistant to government-led currency devaluation.
- Cross-border accessibility allows citizens to preserve wealth outside local economic systems.
Comparison to Other Inflation Hedges
Unlike gold or foreign currencies, which face storage challenges and accessibility issues, bitcoin:
- Can be secured and transported digitally.
- Is divisible into tiny fractions (satoshis), allowing microeconomic activity.
- Cannot be confiscated if stored properly with secure keys.
- Is accessible to anyone with internet access.
Fostering Entrepreneurship and Economic Development
Bitcoin is enabling new business models and entrepreneurship across Africa:
Bitcoin-Based Businesses
- Yellow Card, a leading African digital currency exchange, has raised $89.5 million to facilitate adoption.
- Tando, a Kenyan Startup, has developed an integration with Kenya’s mobile money service to help locals spend bitcoin.
- African Bitcoin miners are utilizing stranded renewable energy resources, particularly in Ethiopia, which has contributed 2.25% of the global Bitcoin hash rate.
Case Study: Kibera, Kenya
In Kibera, Kenya’s largest informal settlement, the Afribit project is using bitcoin as a tool for financial empowerment. This initiative has become a model for bitcoin adoption in underserved communities, creating economic opportunities where traditional banking has failed.
Cross-Border
Bitcoin enables frictionless cross-border trade by:
- Eliminating currency conversion challenges
- Reducing payment settlement times from days to minutes
- Removing intermediaries and associated costs
- Enabling trade with countries suffering from banking restrictions
Case Studies of Success
Bitcoin Ekasi in South Africa
Bitcoin Ekasi is a circular economy project in a South African township that has successfully integrated bitcoin into daily economic activities. The initiative has deepened community ties and provided financial services to previously underserved populations.
Tando in Kenya
Tando has developed a solution that allows anyone in Kenya to easily spend bitcoin by integrating the Lightning Network with existing fiat and mobile money payment rails. This integration makes bitcoin immediately useful for daily transactions without requiring merchants or consumers to understand the underlying technology.
Future Outlook
Bitcoin presents a unique opportunity to address several critical challenges facing African economies. By providing financial inclusion for the unbanked, reducing remittance costs, protecting against inflation, and fostering entrepreneurship, bitcoin can play a transformative role in salvaging and strengthening economic systems across the continent.
Africa’s high mobile phone penetration, youthful tech-savvy population, and entrepreneurial spirit create fertile ground for bitcoin adoption. Countries that recognize this potential and develop supportive regulatory environments will likely see significant economic benefits through increased financial inclusion, reduced transaction costs, and greater economic resilience.
For Africa’s economic future, bitcoin represents not just a technological innovation but a practical solution to longstanding structural challenges. By embracing this technology thoughtfully, African nations have the opportunity to leapfrog traditional financial systems and build more inclusive, resilient economies for the 21st century.















