BitChat isn’t just another encrypted messenger—it’s a paradigm shift that returns messaging to its peer-to-peer roots while leveraging cutting-edge cryptography and mesh networking. Unlike every messaging platform you’ve ever used, BitChat operates without internet connectivity, without centralized servers, and without collecting any personal information.
Understanding how BitChat works reveals a technological breakthrough that could reshape digital communication, particularly in regions facing internet censorship, natural disasters, or government surveillance.
What Makes It Different?
To understand how BitChat works, we must first recognize what it fundamentally changes about messaging. Every popular platform—WhatsApp, Telegram, Signal, iMessage—relies on centralized server infrastructure. Your messages pass through company-controlled servers, creating potential surveillance points, single points of failure, and data honeypots for hackers or governments.
BitChat eliminates this entire paradigm. When you understand how it works, you realize your phone becomes both the client and the server, participating in a decentralized network where messages hop device-to-device until reaching their destination.
This isn’t theoretical—BitChat has already proven its value during protests in Indonesia and Nepal, where internet shutdowns couldn’t silence communication because BitChat users formed offline mesh networks.
The core innovation centers on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) mesh networking—technology that allows smartphones to form ad-hoc communication networks without infrastructure. Each device running BitChat acts as a relay point, extending the network’s reach far beyond the typical 30-100 meter Bluetooth range.
Messages automatically route through multiple devices until they reach their intended recipient, creating a resilient communication layer that operates independently of traditional telecommunications or internet infrastructure.
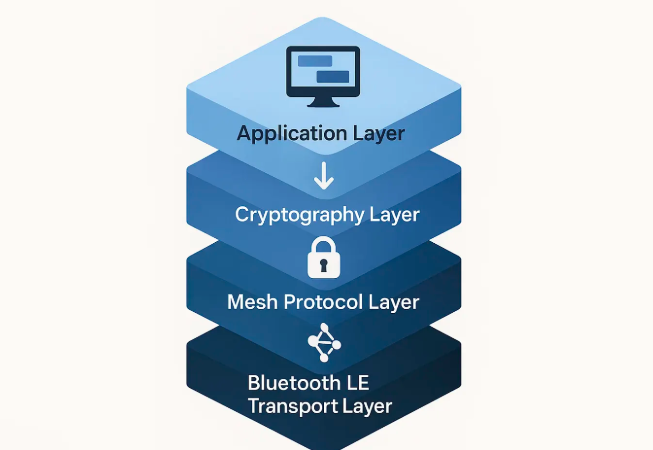
The Dual Transport Architecture
BitChat reveals a sophisticated dual-transport system designed for maximum flexibility and reliability.
The Bluetooth Mesh Network: Offline Foundation
The primary layer of how BitChat works utilizes Bluetooth Low Energy mesh networking for local, offline communication. This isn’t simple point-to-point Bluetooth you’re familiar with—it’s a mesh topology where every device simultaneously acts as sender, receiver, and relay node.
Here’s the step-by-step process of how it works in mesh mode:
- Message Creation: User writes a message in the BitChat interface.
- Encryption: The Message is immediately encrypted using the recipient’s public key.
- Routing Metadata Addition: Anonymous routing information is attached, telling nearby devices where to forward the message.
- Local Broadcasting: Message broadcasts via Bluetooth to all nearby BitChat devices (typically within 30-100 meters).
- Store-and-Forward Relay: Devices that receive the message check if they’re the intended recipient; if not, they store the encrypted message temporarily and re-broadcast it to nearby devices.
- Multi-Hop Propagation: This process repeats, with messages hopping device-to-device across the mesh network.
- Recipient Delivery: When the message reaches a device with the matching decryption key, it’s delivered and displayed.
- Ephemeral Deletion: Messages automatically delete after delivery, leaving no permanent trace.
The mesh network formed by devices creates what researchers call an “ad-hoc, ephemeral communication layer” that requires zero infrastructure.
The Internet Layer: Extended Reach
While offline mesh networking defines how BitChat works locally, the application includes a complementary internet-based transport layer for longer-distance communication. This dual architecture is crucial for understanding how it works across different scenarios.
When devices are internet-connected, BitChat utilizes Nostr protocol (Notes and Other Stuff Transmitted by Relays)—a decentralized messaging protocol inspired by Bitcoin’s architecture. Messages sent through this layer use NIP-17 encryption (Nostr Implementation Possibility 17), which implements “gift-wrapped” private messages that hide metadata even from relay servers.
How BitChat works in internet mode:
- Messages are encrypted identically to mesh mode.
- Instead of Bluetooth broadcast, messages are sent to decentralized Nostr relays.
- Multiple relays store encrypted messages temporarily.
- Recipients query relays for messages addressed to their public keys.
- No single relay has complete network visibility.
- Messages remain end-to-end encrypted throughout transit.
This dual-transport architecture offers unprecedented flexibility: automatically use Bluetooth mesh when offline or in proximity to other users, seamlessly switch to internet relay when connected online, maintain identical encryption and privacy guarantees across both transports, and enable global reach without sacrificing local resilience.
The Cryptographic Foundation
BitChat implements military-grade encryption that ensures your messages remain private even when relaying through dozens of unknown devices.
Key Generation and Exchange
The foundation begins with Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), specifically the Curve25519 algorithm developed by renowned cryptographer Daniel J. Bernstein. This is the same cryptographic curve trusted by Signal, WhatsApp, and numerous government secure communication systems.
When you first open BitChat:
- Your device generates a random Ed25519 private key—a 256-bit number that serves as your identity.
- Mathematical operations derive a corresponding public key from this private key.
- The public key becomes your BitChat identity/address (similar to a Bitcoin address).
- Your private key never leaves your device and is protected by your device’s secure enclave or keystore.
This explains how BitChat works without accounts—your cryptographic key pair is your identity. No email, no phone number, no personal information required.
Message Encryption: X25519 and AES-256-GCM
The process explaining how BitChat works to encrypt individual messages combines two powerful cryptographic primitives:
Step 1: Key Exchange via X25519
When you send a message to another BitChat user, the application performs an Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) key exchange using X25519:
- Your device combines your private key with the recipient’s public key.
- The recipient’s device combines their private key with your public key.
- Through mathematical properties of elliptic curves, both devices arrive at the same shared secret.
- This shared secret becomes the encryption key for your conversation.
- Critically, this shared secret is never transmitted—it’s computed independently by both parties.
Step 2: Symmetric Encryption via AES-256-GCM
With the shared secret established, how BitChat works for actual message encryption uses AES-256-GCM (Advanced Encryption Standard with 256-bit keys in Galois/Counter Mode):
- Messages are encrypted using the shared secret as the AES key.
- GCM mode provides both confidentiality (encryption) and authenticity (verification that messages haven’t been tampered with).
- Each message includes a unique nonce (number used once) preventing replay attacks.
- The resulting ciphertext is cryptographically protected with 256-bit security—considered unbreakable with current technology.
This two-layer approach explaining how BitChat works ensures perfect forward secrecy: even if someone later obtains your private key, they cannot decrypt previous messages because each session uses ephemeral keys that are destroyed after use.
Channel Encryption: Password-Protected Groups
How BitChat works for group chats (called “channels”) implements different but equally robust encryption:
- Channels can be public (anyone can join) or password-protected.
- Password-protected channels use Argon2id for key derivation—a memory-hard function that resists brute-force attacks.
- The derived key encrypts all channel messages using AES-256-GCM.
- Even other BitChat users cannot decrypt channel messages without knowing the password.
Identity Verification: Ed25519 Signatures
A critical aspect of how BitChat works involves proving message authenticity. Each message includes an Ed25519 digital signature:
- Sender signs the message with their private key.
- Recipients verify the signature using the sender’s public key.
- This proves the message came from the claimed sender and wasn’t modified in transit.
- Signatures prevent impersonation attacks, even in the open mesh network.
This comprehensive cryptographic stack explaining how BitChat works provides security equivalent to—or exceeding—platforms like Signal, while operating in a completely decentralized, server-free environment.
Privacy Features Beyond Encryption
Encryption explains only part of how BitChat works to protect privacy. The application includes numerous additional privacy features that set it apart from competitors.
No Personal Information Required
The most obvious aspect of how BitChat works regarding privacy: zero personal data collection:
- No email address required.
- No phone number required.
- No username required (your public key is your identifier).
- No contact list upload.
- No analytics or telemetry.
- No server-side storage of messages.
Your BitChat identity is a cryptographic key pair—nothing more. This fundamentally changes how BitChat works compared to platforms like Signal (requires phone number) or Telegram (requires phone number or username).
Ephemeral Messages and Auto-Deletion
How BitChat works for message persistence prioritizes privacy over convenience:
- Messages automatically delete after being delivered and read.
- No permanent message history stored by default.
- Users can optionally save specific messages locally.
- Relay devices delete encrypted messages after forwarding or after timeout.
- Even if someone physically seizes your device, they find no message history.
This “disappearing by default” approach reflects a philosophy that private communication shouldn’t leave permanent records.
Panic Mode: Emergency Data Erasure
A critical privacy feature in how BitChat works is Panic Mode—instant data destruction:
- Triple-tap the BitChat logo.
- All messages, contacts, and cryptographic keys are immediately deleted.
- App returns to pristine first-use state.
- Irreversible and instantaneous.
This feature works for activists, journalists, or anyone facing potential device confiscation. During Hong Kong’s 2019 protests, demonstrators used similar features in apps like Bridgefy and Telegram—BitChat’s implementation improves upon these with cryptographic key deletion that makes recovery truly impossible.
No Metadata Exposure
Traditional messaging platforms may encrypt message content but expose metadata—who communicates with whom, when, and how frequently. This metadata often reveals more than message content itself.
How BitChat works to protect metadata:
- Mesh relay means no centralized server logs who connects to whom.
- Messages don’t include sender identity in routing headers (only destination).
- Timing analysis is difficult because messages may sit in relay queues for indeterminate periods.
- Internet-mode uses Nostr’s gift-wrapped encryption hiding sender/recipient even from relays.
- Geohash-based ephemeral keys mean your identity changes as you move.
This comprehensive metadata protection explains how BitChat works to provide privacy superior to even Signal, which must maintain some metadata for message delivery.
Open Source Transparency
How BitChat works can be independently verified because the entire codebase is open source on GitHub:
- Security researchers can audit the cryptographic implementation.
- Users can verify no backdoors or tracking exist.
- Community can contribute improvements.
- Transparency builds trust that commercial messaging platforms cannot match.
Technical Limitations and Challenges
No technology is perfect. Understanding how BitChat works requires acknowledging its limitations and the trade-offs inherent in its design.
Range and Density Requirements
How BitChat works depends on network effect:
- Requires multiple nearby users to form effective mesh.
- In low-density areas, range is limited to direct Bluetooth (30-100m).
- Messages cannot reach distant recipients without sufficient relay nodes.
- Early adoption phase means limited current user base.
However, as more people adopt BitChat, the mesh becomes increasingly powerful—a self-reinforcing network effect where each additional user extends everyone else’s range.
Battery and Performance Impact
How BitChat works requires continuous Bluetooth scanning and relay:
- BLE is energy-efficient but not zero-cost.
- Users report 5-15% increased battery drain depending on usage.
- Relay traffic consumes bandwidth and processing power.
- On older devices, performance may be noticeably impacted.
BitChat implements optimizations to minimize this, but physics cannot be completely overcome—maintaining a mesh network requires energy.
Message Delivery Uncertainty
Unlike centralized platforms:
- No delivery confirmation for multi-hop mesh messages.
- Messages may fail to reach recipient if mesh is fragmented.
- Delay can be significant as messages hop through relay nodes.
- No global message status like “read receipts” or “delivered” indicators.
This uncertainty is the trade-off for privacy and decentralization. Users must accept that messages may not arrive instantly (or at all) compared to server-based platforms.
Security Considerations
While BitChat’s encryption is robust, understanding how BitChat works reveals potential attack vectors:
Malicious Relay Nodes: Attackers could run many BitChat devices to analyze network traffic patterns (though they cannot decrypt messages).
Denial of Service: Flooding the mesh network with garbage messages could disrupt legitimate communication.
Social Engineering: Since there’s no centralized identity verification, impersonation is possible if public keys aren’t verified through out-of-band channels.
Security researchers have published detailed analyses of how BitChat works from a security perspective, noting these concerns while acknowledging the fundamental cryptography remains sound.
Getting Started
Understanding how BitChat works theoretically is valuable, but using it is straightforward. Here’s how to get started:
Installation
BitChat is available on multiple platforms:
Android
- Download from Google Play Store
- Or install APK from official website
- Requires Android 8.0 or higher
- ~15MB download
iOS
- Download from Apple App Store
- Requires iOS 14.0 or higher
- ~20MB download
Planned Features and Roadmap
The BitChat development team has outlined how BitChat will work with future enhancements:
File Sharing
- Current version handles text; future versions will support media.
- File fragmentation and deduplication for efficient mesh transfer.
- Encrypted file storage with decentralized hosting.
Voice and Video
- Real-time encrypted voice calls over mesh network.
- Video conferencing without centralized servers.
- Adaptive quality based on mesh bandwidth availability.
Bitcoin Integration
- Native Lightning Network payments within BitChat.
- Send satoshis directly in messages (already functioning in beta).
- Tipping, commerce, and value-for-value communication.
- True “money over messaging” layer.
Enhanced Routing
- Machine learning optimization of mesh routes.
- Predictive caching based on movement patterns.
- Integration with other mesh protocols (LoRa, WiFi Direct).
Dorsey has consistently advocated for what he calls “permissionless innovation”—systems that don’t require gatekeepers’ approval to use or extend.
The open-source codebase allows independent security audits, and multiple analyses have confirmed the encryption implementation is correct. However, as with any security tool, operational security matters: verify public keys, use Panic Mode appropriately, and understand that mesh relay patterns could potentially reveal some metadata even though messages remain encrypted.















