Bitcoin mining is no longer a geeky side hustle—it’s a global business where success depends on data-driven decision-making.
Among the key metrics every miner should understand are hashprice and hashvalue, two terms that define how profitable your hardware truly is.
In this guide, we’ll break down what these terms mean, how they interact, and how miners can use them to make smarter operational, financial, and strategic decisions.
From Hashrate to Revenue: The Basics
Mining involves powerful computing machines (ASICs) competing to find random numbers. Tell me a number between 1 and infinity, if you guessed correct, you win the next bitcoin block. That’s how simple bitcoin mining truly is. But manual guessing is too slow hence miners throw in millions of guesses per second The faster your rig (measured in terahashes per second, or TH/s), the higher your chances. Or, in case you connect your miner to a pool, more TH/s means higher payout.
However, just hashing faster doesn’t guarantee profit. What matters is how much each unit of hashing power earns in Bitcoin and fiat terms — that’s where hashprice and hashvalue come in.
What is Hashprice?
Hashprice measures how much miners earn in USD for each terahash of computing power per day (USD/TH/day).
It’s essentially your revenue rate — like your miner’s daily paycheck in dollar terms.
Hashprice is influenced by:
- Bitcoin price: When BTC’s market price rises, your earnings per TH generally go up.
- Transaction fees: High network usage means more fees paid to miners.
- Network difficulty: As difficulty climbs, the same hardware earns less BTC.
- Block rewards: Every halving event cuts rewards by 50%, reducing post-halving hashprice.
Why it matters:
Hashprice is key for forecasting revenue in fiats. It helps miners decide when to expand, throttle operations, or adjust power contracts.
What is Hashvalue?
Hashvalue, by contrast, measures how much Bitcoin (in BTC) your rig earns per terahash per day (BTC/TH/day).
It tracks earnings in Bitcoin units, before currency conversion.
Hashvalue depends on:
- Block rewards: Currently 3.125 BTC per block (as of 2025).
- Transaction fees: A surge in on-chain activity raises hashvalue.
- Network difficulty: More competition = less BTC per terahash.
Hashvalue cuts through the noise of market price swings. Even when BTC/USD fluctuates wildly, your hashvalue tells you how much coin your hardware is actually earning.
Hashprice vs Hashvalue
| Metric | Measured In | Affected By BTC Price | Core Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hashprice | USD/TH/day | Yes | Projecting fiat revenue & profitability |
| Hashvalue | BTC/TH/day | No | Measuring network-level mining efficiency |
Understanding both provides miners with full visibility: hashprice for cashflow forecasts and hashvalue for production efficiency.
Why These Metrics Matter
Mining is a balancing act between revenue, energy costs, and operational efficiency.
With hashprice and hashvalue, miners can:
- Plan operations around energy rate changes and hashrate competition.
- Optimize hardware selections for efficiency (measured as hash rate per watt).
- Time BTC sales — for instance, holding mined BTC when fiat hashprice drops but BTC price is expected to rise.
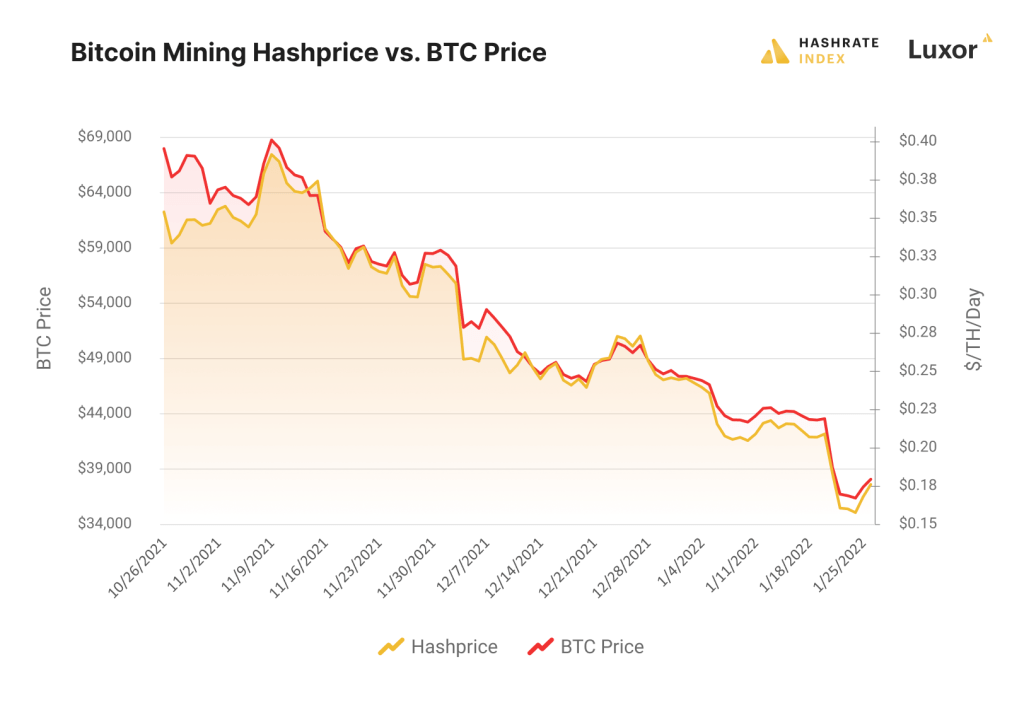
How Hashprice Fluctuates
Hashprice is dynamic because it reflects a living ecosystem.
When Bitcoin’s price spikes, transaction volume often grows, raising fees and boosting hashprice. But when difficulty adjusts upward — typically every two weeks — payouts per TH can dip.
Common drivers of hashprice swings include:
- Bitcoin price volatility
- Seasonal shifts in network hashrate (e.g., during hydro power seasons in mining regions)
- Changes in transaction congestion (e.g., from Ordinals or BRC-20 activity)
Strategies for Miners: Navigating Hashprice Volatility
Stability in mining comes from control. While hashprice is volatile, miners can take strategic steps to protect profitability.
1. Harness cheap or renewable power:
Electricity is often 70% of mining costs. Wind, hydro, or surplus energy contracts reduce exposure to price swings.
2. Accumulate rather than sell at lows:
Miners maintaining BTC reserves during low-hashprice periods can later capitalize on bull markets.
3. Use managed mining services:
Companies like Sazmining handle infrastructure, maintenance, and energy optimization — turning raw hashrate into predictable yield.
4. Check profitability tools:
Miners can use calculators (like Bitbo or Sazmining) to simulate earnings based on electricity cost, power efficiency, and network difficulty.
Turning Volatility into Opportunity
Hashprice fluctuations aren’t a curse—they’re part of mining’s rhythm.
By tracking both hashprice and hashvalue, miners can separate network performance (BTC output) from market noise (USD fluctuations).
Over time, this clarity helps miners make smarter power deals, hardware upgrades, and treasury decisions.
The Takeaway
Bitcoin mining profitability isn’t random — it’s measurable.
Hashprice tells you how much your hashrate earns in dollars today; hashvalue tells you how much Bitcoin your rigs produce regardless of price swings.
In a volatile industry, miners who understand these metrics don’t just survive — they optimize, strategize, and compound their edge over less data-driven competitors.
Because in Bitcoin mining, the most valuable resource isn’t energy — it’s information.